
May 23 2023
Introduction:
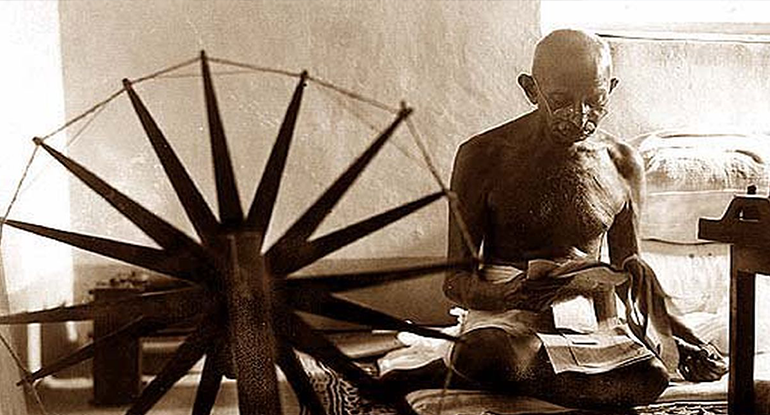
Mahatma Gandhi, the epitome of nonviolent resistance and leader of India’s independence movement, remains one of the most influential figures in the world’s history. His life story is not just about political activism; it’s a saga of personal transformation, unwavering conviction, and the power of peaceful protest to bring about profound societal change. Let’s delve into the remarkable journey of this visionary leader.
Early Life and Influences:
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, a coastal town in present-day Gujarat, India. His upbringing was rooted in Hindu traditions and values, shaped by the teachings of his devout mother and the influence of Jainism through his family connections.
Gandhi’s formative years were marked by a quest for knowledge and a sense of justice. He traveled to London in 1888 to study law, a decision that exposed him to Western culture and ideas. However, it was during his time in South Africa, where he lived from 1893 to 1914, that Gandhi’s activism was ignited.
Activism in South Africa:
In South Africa, Gandhi experienced firsthand the brutal realities of racial discrimination and injustice. He was appalled by the discriminatory treatment of Indians and other non-white communities under British colonial rule. This experience became a turning point in his life as he began to advocate for the rights of oppressed minorities.
Gandhi’s approach to activism in South Africa was characterized by nonviolent resistance, which he termed “Satyagraha” or truth-force. Through boycotts, strikes, and civil disobedience campaigns, Gandhi sought to challenge unjust laws and policies without resorting to violence. His philosophy emphasized the power of moral courage and self-sacrifice to win over adversaries and effect lasting change.
Return to India and Leadership of the Independence Movement:
In 1915, Gandhi returned to India, bringing with him the lessons and principles of Satyagraha learned in South Africa. He quickly emerged as a prominent leader in India’s struggle for independence from British rule. Gandhi’s leadership style was marked by simplicity, humility, and a deep sense of empathy for the marginalized and oppressed.
One of Gandhi’s most significant contributions to the independence movement was the concept of swaraj, or self-rule. He envisioned a free India where every individual would have the opportunity to participate in the governance of their country, regardless of caste, creed, or religion.
Throughout the 1920s and 1930s, Gandhi led several nonviolent campaigns against British rule, including the Non-Cooperation Movement, the Salt March, and the Quit India Movement. These campaigns mobilized millions of Indians from all walks of life, demonstrating the power of mass civil disobedience in challenging colonial authority.
Legacy and Global Impact:
Mahatma Gandhi’s legacy extends far beyond the borders of India. His philosophy of nonviolence and his commitment to social justice inspired countless movements for civil rights, freedom, and equality around the world. Leaders such as Martin Luther King Jr., Nelson Mandela, and Cesar Chavez drew inspiration from Gandhi’s teachings and applied them in their own struggles for justice and liberation.
Gandhi’s influence transcends political boundaries and continues to resonate in contemporary discussions on peacebuilding, conflict resolution, and human rights. His emphasis on dialogue, empathy, and the inherent dignity of every individual remains as relevant today as it was during his lifetime.

The principles and values advocated by Mahatma Gandhi are upheld and implemented. These principles revolve around nonviolence (ahimsa), truthfulness (satyagraha), self-reliance, simplicity, and the pursuit of social justice. Here are some key aspects of what might be practiced in a Gandhian society.
GANDHIAN SOCIETY 1412, Oak Tree Road Iselin, New Jersey-08830
(+1) 732 407 5013
info@gandhiansociety.org
Our Maps
 Users Today : 9
Users Today : 9